February 14, 2022 feature
Switching plasmonic nanogaps between classical and quantum regimes
Quantum plasmonics is and its interaction with matter at the nanoscale. While intriguing, they are difficult to regulate on account of the lack of proper surface spaces to reversibly actuate sub-1 nanometer gaps. In the field of extreme , researchers have shown how nanogap plasmons can support reliable field enhancements to provide unique opportunities to access a single molecule for strong coupling, and a single atom for . In a new report now published on Science Advances, Chi Zhang and a team of scientists in physics, science and technology in Wuhan, China, showed that supramolecular systems made of can reversibly switch gap plasmons of gold nanoparticles between classical and quantum tunneling regions through supramolecular interactions. The outcomes showed detailed plasmon shift near the quantum tunneling limit to fit well with classical and quantum-corrected models. The team noted how plasmonic hot electronic tunneling in quantum tunneling regions increased conductance in the nanogaps to form a promising prototype of optical tunable, across the classical and quantum regimes.
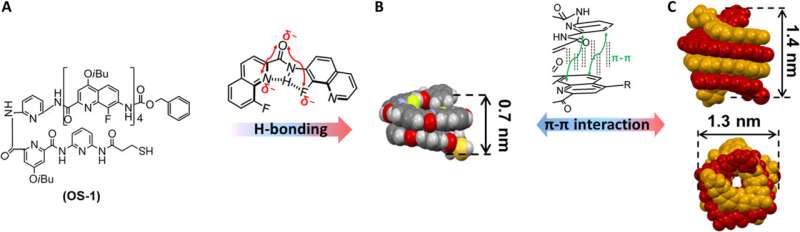
Forming oligoamide sequences
Due to its wide range of applications in nano-optics, materials science, and energy harvesting, plasmonics has thrived in vibrant and interdisciplinary fields . Since many of the superior plasmonic properties are related to their large electric field confinement and small mode volume, quantum physicists can engineer as a hot topic in . The nanogap plasmon is very sensitive to the and can form a nanoscale '' for , , and determine the and thickness of with resolutions extending to the sub-picometer range. However, it is still challenging to reversibly switch nanogaps across the quantum tunneling limit (a quantum mechanical phenomenon, where a wavefunction can propagate through a potential barrier) relative to mechanical models, due to the absence of a . As a result, many fabrication methods aiming to form quantum mechanical effects for plasmons in nanogap structures are based on nanotechnology. Supramolecular systems at the sub-nanometer scale can provide unique opportunities to access the quantum limit. To facilitate squeezing into the quantum plasmonic regime, Zhang et al. designed an artificial system to switch across sub-nanometer gaps across the . In this work, they used ; a set of supramolecular systems engineered to fit around the nanometer-range, to facilitate quantum plasmonic transitions for quantum optoelectronic devices.

The team chemically engineered repeating units of oligoamide sequences to fit the structures just below the quantum limit. Placing them in plasmonic nanogaps enormously benefitted reversible switching between classical and quantum plasmonic regions, to help shed light on quantum plasmonic transitions and show important implications for quantum devices. During the experiments, Zhang et al. first synthesized an oligoamide sequence-1 (OS-1) bearing a thiol group at its and then made a self-assembled monolayer of double-helix OS-1 on gold films by drop-casting gold nanoparticles on top of gold-sulfide bonds. They then tuned the gap size by changing their conformations after sandwiching antiparallel double helices between gold nanoparticles and the mirror. The scientists characterized the gold nanoparticles on mirror (NPoMs) with . The results indicated solvent-driven motion therefore they changed the polarity of solvents by adjusting the constituent ratio of methanol and dichloromethane as software. Zhang et al. also noted the equilibrium of single and double helices of oligoamide sequences to depend on the temperature therefore the process could be reversed by cooling. The team reproduced the thermal-induced plasmon switch for a few cycles; the gold NPoM (nanoparticles on mirror) plasmonic ruler provided a simple mechanism to monitor the assembly and disassembly of double helices at sub-angstrom resolution via scattering spectroscopy.
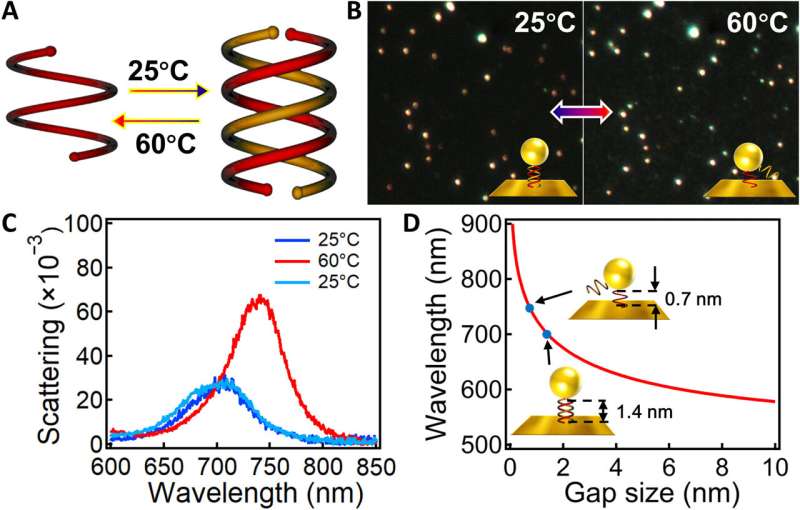
Simulations and optimized experiments
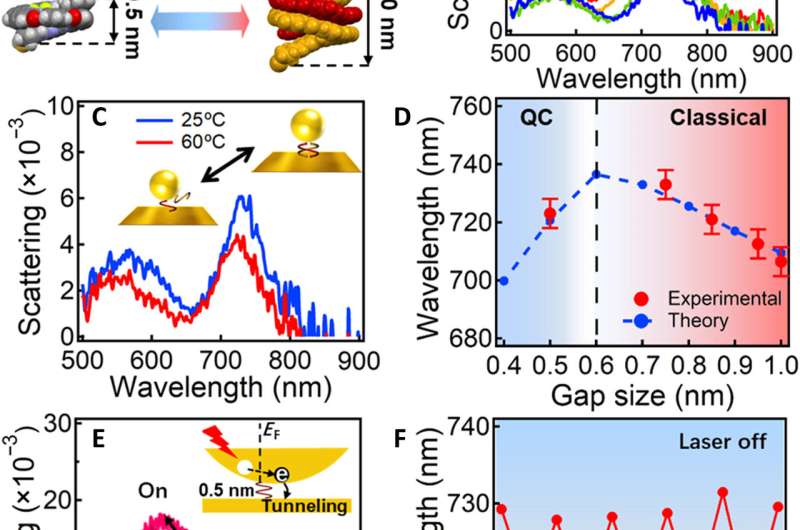
To further reduce the gap size below the quantum tunneling limit, Zhang et al. chose the shorter oligoamide sequence-2 (OS-2) with only two units as the spacer self-assembled monolayer. The resulting OS-2 formed a single helical strand with a height of 1.0 nm, to switch right across the . By increasing the ratio of methanol and dichloromethane, Zhang et al. noted as a result of contracting double helices. The team next simulated the correlation of the methanol content and double-helix size via SPARTAN software, which they used as the gap size of the corresponding plasmon peak. The real gap size could be smaller than the simulated value. The plasmon peaks agreed with the quantum-corrected model to indicate a quantum tunneling limit of about 0.6 nm—consistent .
Quantum tunneling
During the experiments, they conducted hot electron tunneling via laser excitation to contribute to the conductance of nanogaps. Zhang et al. noted a blue shift of the coupled plasmons upon laser irradiation, which switched back by turning the laser off. They used a continuous wave laser with low power, where temperature rise in the nanogap was only 0.2 degrees Celsius, without effecting molecular conformations. The team robustly reproduced the switching for many cycles by switching the laser on and off to rule out the possibility of the nanogap bridging effect induced by . For control experiments, Zhang et al. used a single-strand OS-1 in a contrast sample as the gap medium, and did not observe photoswitching of plasmons. They then calculated the conductivity increase of the nanogaps that contributed to hot electron transfer relative to the number of hot electrons produced by laser excitation in the presence of OS-2 molecules. During calculations, the team considered electric charge and mobility of hot electrons in the OS-2 molecules, where total conductance increased from hot electrons for approximate . The outcome agreed well with experiments to represent spectral characterization of quantum conductance states, with great implications for quantum optoelectronic devices.
Outlook
In this way, Chi Zhang and colleagues engineered oligoamide sequences (OS) based on supramolecular systems with a series of repeating building blocks to accommodate different gap sizes for different ranges of plasmonic switching. The supramolecular system functions as a nanoactuator at plasmonic nanogaps for spring-like nano-actuation of gold nanoparticles on mirror (NPoM), with potential applications for nanomachines. The plasmonic system can be used as a sensor for temperature or solvents, based on the shift of plasmon resonances. The setup is applicable as a precise plasmonic ruler to monitor the changing oligoamide sequence conformation by measuring scattering spectra of each individual gold nanoparticle to form a fundamental instrument/tool in supramolecular chemistry.
More information: Chi Zhang et al, Switching plasmonic nanogaps between classical and quantum regimes with supramolecular interactions, Science Advances (2022).
Jeffrey N. Anker et al, Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors, Nature Materials (2008).
Journal information: Science Advances , Nature Materials
© 2022 Science X Network